Testicular Cancer Screening
Finding cancer in its earliest stage offers the best chance of successful treatments. That’s why Montefiore Einstein Comprehensive Cancer Center is passionate about screenings for testicular cancer and many other cancer types at our NCI-designated cancer center.
Finding testicular cancer early can make it easier to treat. If you have certain risk factors that increase your chance of developing testicular cancer—such as an undescended testicle, previous germ cell tumor in one testicle, or family history—you should conduct monthly self-exams and talk to your provider about screening.
At our cancer center, we’re at the forefront of new and innovative methods for treating testicular cancer. Our goal is to eliminate the cancer, normalize urinary function and restore sexual function. Our patient recovery program supports these goals while providing access to nurse-led support groups.
For more than 50 years, Montefiore Einstein Comprehensive Cancer Center has been a leader in the research, diagnosis and treatment of over 200 types of cancer. Turn to us for comprehensive cancer screening.

Cancer Clinical Trials
- Blood & Bone Marrow Cancers
- Brain, Spine & Central Nervous System Cancers
- Breast Cancer
- Childhood Cancers
- Endocrine System Cancers
- Gastrointestinal (GI) Cancers
- Genitourinary (GU) & Urologic Cancers
- Gynecologic Cancers
- Head & Neck Cancers
- Kaposi Sarcoma & AIDS-Related Cancers
- Lung & Chest Cancers
- Prostate Cancer
- Sarcomas
- Skin Cancer
As an NCI-designated comprehensive cancer center, Montefiore Einstein Comprehensive Cancer Center supports the mission and guidelines of the National Cancer Institute (NCI). The following information about types of cancer, prevention and treatments is provided by the NCI.
Testicular Cancer Screening (PDQ®)–Patient Version
What Is Screening?
Screening is looking for cancer before a person has any symptoms. This can help find cancer at an early stage. When abnormal tissue or cancer is found early, it may be easier to treat. By the time symptoms appear, cancer may have begun to spread.
Scientists are trying to better understand which people are more likely to get certain types of cancer. They also study the things we do and the things around us to see if they cause cancer. This information helps doctors recommend who should be screened for cancer, which screening tests should be used, and how often the tests should be done.
It is important to remember that your doctor does not necessarily think you have cancer if he or she suggests a screening test. Screening tests are given when you have no cancer symptoms.
If a screening test result is abnormal, you may need to have more tests done to find out if you have cancer. These are called diagnostic tests.
General Information About Testicular Cancer
Key Points
- Testicular cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles.
- Testicular cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in men aged 20 to 39 years.
- Testicular cancer can usually be cured.
- A condition called cryptorchidism (an undescended testicle) is a risk factor for testicular cancer.
Testicular cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles.
The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands inside the scrotum (a sac of loose skin that lies directly below the penis). The testicles are held within the scrotum by the spermatic cord. The spermatic cord also contains the vas deferens and vessels and nerves of the testicles.
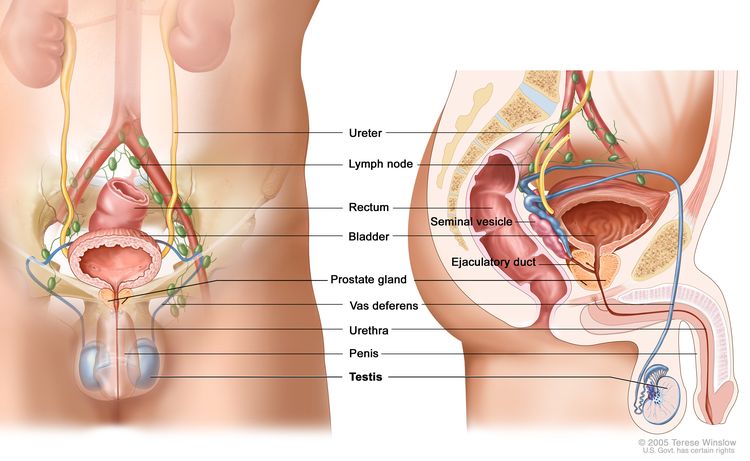
Anatomy of the male reproductive and urinary systems, showing the testicles, prostate, bladder, and other organs.
The testicles are the male sex glands and make testosterone and sperm. Germ cells in the testicles make immature sperm. These sperm travel through a network of tubules (tiny tubes) and larger tubes into the epididymis (a long coiled tube next to the testicles). This is where the sperm cells mature and are stored.
Almost all testicular cancers start in the germ cells. The two main types of testicular germ cell tumors are seminomas and nonseminomas.
Learn more about testicular cancer at Testicular Cancer Treatment.
Testicular cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in men aged 20 to 39 years.
Testicular cancer is the most common cancer in men between the ages of 20 to 39 years, with the highest rates between ages 25 to 34 years. The racial and ethnic groups with the highest rates of testicular cancer include non-Hispanic White men, non-Hispanic American Indian men, and Alaska Native men.
Testicular cancer can usually be cured.
Although the number of new cases of testicular cancer has doubled in the last 40 years, the number of deaths caused by testicular cancer has decreased greatly because of better treatments. Testicular cancer can usually be cured, even in late stages of the disease. Learn more about testicular cancer at Testicular Cancer Treatment.
A condition called cryptorchidism (an undescended testicle) is a risk factor for testicular cancer.
Anything that increases a person's chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Not every person with one or more of these risk factors will develop testicular cancer, and it will also develop in some people who don't have any known risk factors. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for testicular cancer include:
- having cryptorchidism
- having a testicle that is not normal, such as a small testicle that does not work the way it should
- having testicular carcinoma in situ
- being a White man
- having a personal or family history of testicular cancer
- having Klinefelter syndrome
Men who have cryptorchidism, a testicle that is not normal, or testicular carcinoma in situ have an increased risk of testicular cancer in one or both testicles and need to be followed closely.
Testicular Cancer Screening
Key Points
- Tests are used to screen for different types of cancer when a person does not have symptoms.
- There is no standard or routine screening test for testicular cancer.
- Screening tests for testicular cancer are being studied in clinical trials.
Tests are used to screen for different types of cancer when a person does not have symptoms.
Scientists study screening tests to find those with the fewest harms and most benefits. Cancer screening trials also are meant to show whether early detection (finding cancer before it causes symptoms) helps a person live longer or decreases a person's chance of dying from the disease. For some types of cancer, the chance of recovery is better if the disease is found and treated at an early stage.
There is no standard or routine screening test for testicular cancer.
There is no standard or routine screening test used for early detection of testicular cancer. Most often, testicular cancer is first found by men themselves, either by chance or during self-exam. Sometimes the cancer is found by a doctor during a routine physical exam.
No studies have been done to find out if testicular self-exams, regular exams by a doctor, or other screening tests in men with no symptoms would decrease the risk of dying from this disease. However, routine screening probably would not decrease the risk of dying from testicular cancer. This is partly because testicular cancer can usually be cured at any stage. Finding testicular cancer early may make it easier to treat. Patients who are diagnosed with testicular cancer that has not spread to other parts of the body may need less chemotherapy and surgery, resulting in fewer side effects.
If a lump is found in the testicle by the patient or during a routine physical exam, tests may be done to check for cancer. Some tests have risks and may cause anxiety.
Screening tests for testicular cancer are being studied in clinical trials.
Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCI’s clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
About This PDQ Summary
About PDQ
Physician Data Query (PDQ) is the National Cancer Institute's (NCI's) comprehensive cancer information database. The PDQ database contains summaries of the latest published information on cancer prevention, detection, genetics, treatment, supportive care, and complementary and alternative medicine. Most summaries come in two versions. The health professional versions have detailed information written in technical language. The patient versions are written in easy-to-understand, nontechnical language. Both versions have cancer information that is accurate and up to date and most versions are also available in Spanish.
PDQ is a service of the NCI. The NCI is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). NIH is the federal government’s center of biomedical research. The PDQ summaries are based on an independent review of the medical literature. They are not policy statements of the NCI or the NIH.
Purpose of This Summary
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about testicular cancer screening. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Reviewers and Updates
Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date. These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary ("Updated") is the date of the most recent change.
The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the PDQ Screening and Prevention Editorial Board.
Clinical Trial Information
A clinical trial is a study to answer a scientific question, such as whether one treatment is better than another. Trials are based on past studies and what has been learned in the laboratory. Each trial answers certain scientific questions in order to find new and better ways to help cancer patients. During treatment clinical trials, information is collected about the effects of a new treatment and how well it works. If a clinical trial shows that a new treatment is better than one currently being used, the new treatment may become "standard." Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Clinical trials can be found online at NCI's website. For more information, call the Cancer Information Service (CIS), NCI's contact center, at 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
Permission to Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as “NCI’s PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: [include excerpt from the summary].”
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Screening and Prevention Editorial Board. PDQ Testicular Cancer Screening. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/types/testicular/patient/testicular-screening-pdq. Accessed <MM/DD/YYYY>. [PMID: 26389226]
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author(s), artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Disclaimer
The information in these summaries should not be used to make decisions about insurance reimbursement. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.gov on the Managing Cancer Care page.
Contact Us
More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.gov website can be found on our Contact Us for Help page. Questions can also be submitted to Cancer.gov through the website’s E-mail Us.
Updated:
Source URL: https://www.cancer.gov/node/6439/syndication
Source Agency: National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Captured Date: 2013-09-14 09:03:30.0








