Thyroid Nodules and Multinodular Goiters
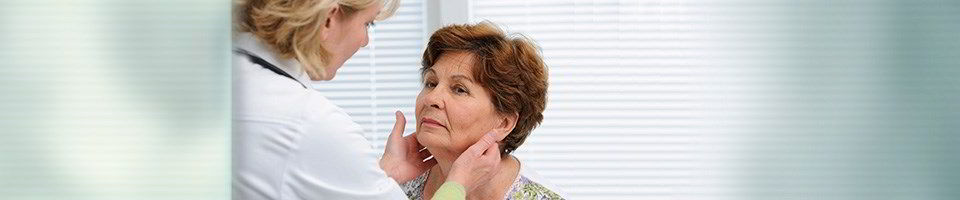
A thyroid nodule is a lump in the thyroid gland. Most nodules are small, but they can vary in size. Some can be easily felt or even seen through the skin, while others are found only via special imaging procedures, such as a thyroid ultrasound. Thyroid nodules are very common. Most of them are innocent or benign, but if you have a thyroid nodule, your doctor might recommend a biopsy.
Thyroid nodules typically do not cause any symptoms or interfere with the normal function of the thyroid gland. Most people don't know they have thyroid nodules until a doctor discovers one during a routine medical exam or coincidentally sees it during a computed tomography (CT) scan, ultrasounds or X-rays done for other reasons.
A goiter refers to any enlargement of the thyroid gland. Sometimes several thyroid nodules will develop in the same person—a condition called multinodular goiter. When this occurs, the thyroid gland is usually enlarged and might cause neck discomfort.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Large nodules and goiters can be felt during an exam or even seen in the front of the neck. Smaller nodules are usually diagnosed by imaging, most commonly a thyroid ultrasound. Your doctor might also order blood tests to make sure the nodule is not affecting your thyroid function. To make sure that the nodule is not cancerous, a doctor might also recommend a fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy.
Treatment is usually not needed in cases where nodules and goiters have been diagnosed as benign and when they do not cause local discomfort. However, these conditions should be monitored over time.
Overactive nodules or multinodular goiters that cause the thyroid to produce too much thyroid hormone, resulting in hyperthyroidism, can be treated with radioactive iodine or surgically removed. Taken as a capsule or in liquid form, radioactive iodine is absorbed by the thyroid gland, causing the nodules to shrink and the signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism to subside, usually within two to three months.
Thyroid surgery might be recommended in thefollowing situations as well:
- If the nodule is found to be malignant or deemed suspicious in biopsy
- If it causes local discomfort, such as pressure in the neck, or causes choking or food to get stuck in the throat
- Patient preference